MATLAB’s Image Processing Tool simplifies complex image analysis tasks. It offers robust functions for filtering, transforming, and analyzing images.
MATLAB’s Image Processing Tool is a versatile software suite designed for both novices and experts. It provides a comprehensive set of tools to perform operations such as image enhancement, noise reduction, geometric transformations, and image segmentation. The intuitive interface and extensive documentation make it accessible, even for those new to image processing.
Its powerful capabilities are backed by MATLAB’s computational efficiency, enabling users to handle large datasets with ease. Whether you are working in medical imaging, remote sensing, or computer vision, this tool can significantly enhance your workflow and deliver precise results.

Credit: www.mathworks.com
Introduction To Matlab For Image Processing
MATLAB is a powerful tool for image processing. It helps in analyzing images and performing complex tasks. Many researchers and engineers use MATLAB. It is known for its flexibility and extensive libraries.
The Role Of Matlab In Creative Image Manipulation
MATLAB allows users to manipulate images creatively. You can transform images in many ways. It supports image enhancement, filtering, and edge detection. This makes it easy to improve image quality.
Users can also combine images. This is helpful for creating unique visuals. MATLAB’s tools make it easy to experiment and innovate. The interactive environment supports rapid prototyping.
Key Features Of Matlab For Image Processing Tasks
- Image Enhancement: Improve the visual quality of images.
- Filtering: Apply various filters to modify images.
- Segmentation: Separate an image into meaningful parts.
- Edge Detection: Identify the edges within images.
- Histogram Processing: Analyze the image intensity distribution.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Image Enhancement | Improves visual quality |
| Filtering | Modifies images with filters |
| Segmentation | Divides images into parts |
| Edge Detection | Finds edges in images |
| Histogram Processing | Analyzes intensity distribution |
MATLAB provides a rich set of functions and tools. These are essential for effective image processing. Users can write custom scripts to automate tasks. This saves time and increases efficiency.
% Example MATLAB Code for Image Enhancement
I = imread('image.jpg'); % Read image
J = imadjust(I,stretchlim(I),[]); % Enhance image
imshow(J); % Display enhanced image
MATLAB is user-friendly. Beginners can start quickly. Advanced users find it powerful. It is a great choice for image processing projects.
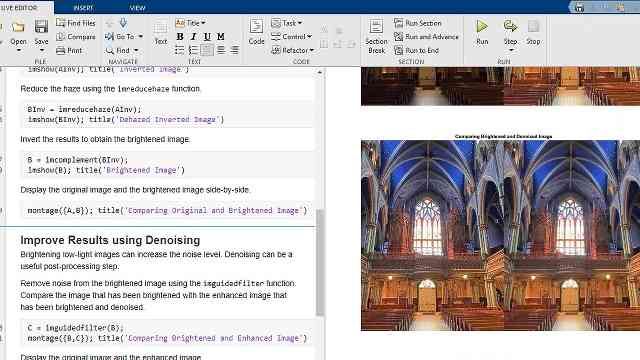
Credit: www.mathworks.com
Getting Started With Matlab
MATLAB is a powerful tool for image processing. It offers numerous functions to manipulate and analyze images. This section will help you get started with MATLAB for image processing.
Setting Up The Matlab Environment
First, you need to install MATLAB. You can download it from the MathWorks website. Follow the installation instructions provided.
Once installed, open MATLAB. You will see the MATLAB desktop. The desktop has several components:
- Command Window: Where you enter commands.
- Workspace: Displays variables you create.
- Current Folder: Shows files in the current directory.
- Editor: Used to write and edit scripts.
Essential Matlab Commands And Syntax For Beginners
Here are some essential MATLAB commands and syntax:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
clc |
Clears the Command Window. |
clear |
Removes all variables from the Workspace. |
imread('image.jpg') |
Reads an image file. |
imshow(image) |
Displays an image. |
size(image) |
Returns the dimensions of the image. |
Here’s an example code to read and display an image:
image = imread('image.jpg');
imshow(image);
To perform basic image processing, you can start with these steps:
- Load the image using
imread. - Display the image using
imshow. - Get image dimensions using
size. - Apply filters or transformations.
These commands are fundamental. They provide a good starting point for beginners.
Fundamentals Of Image Processing
Image processing in Matlab is a powerful tool. It helps transform images into useful information. Understanding the basics is essential for anyone starting in this field.
Types Of Digital Images And Their Properties
There are several types of digital images. Each type has unique properties.
- Grayscale Images: These images contain shades of gray. Each pixel represents a shade from black to white.
- Binary Images: These images have only two colors. Typically, black and white.
- RGB Images: These images use three colors: red, green, and blue. Each pixel has a combination of these colors.
- Indexed Images: These images use a colormap. Each pixel value refers to a color in the colormap.
Basic Image Processing Concepts
Image processing involves various basic concepts. These concepts are foundational.
- Image Acquisition: This is the process of capturing an image.
- Image Enhancement: It improves the visual appearance of an image. Techniques include contrast adjustment and noise reduction.
- Image Restoration: It aims to reconstruct an image. It corrects distortions or degradations.
- Image Segmentation: This process divides an image into parts. Each part represents a meaningful object.
- Image Compression: It reduces the size of an image file. This is done without losing important details.
Understanding these fundamentals is key. They form the base for more advanced image processing tasks in Matlab.
Core Matlab Functions For Image Processing
MATLAB offers robust tools for image processing. These tools help manipulate and analyze images efficiently. Core functions simplify tasks like importing, displaying, converting, and manipulating images.
Importing And Displaying Images
MATLAB makes it easy to import and display images. Use the imread function to read images from files. Display images using the imshow function.
Example:
% Read an image file
img = imread('example.jpg');
% Display the image
imshow(img);
This code snippet reads an image named example.jpg and displays it. The imread function supports various file formats like JPEG, PNG, and TIFF.
Image Conversion And Manipulation
MATLAB provides functions to convert and manipulate images. Convert images from one format to another with ease. Use the rgb2gray function to convert a color image to grayscale.
Example:
% Convert RGB image to grayscale
gray_img = rgb2gray(img);
% Display the grayscale image
imshow(gray_img);
Manipulate images by resizing, rotating, or cropping. Use the imresize function to resize images.
Example:
% Resize the image to half its original size
resized_img = imresize(img, 0.5);
% Display the resized image
imshow(resized_img);
Rotate images using the imrotate function. Crop images with the imcrop function.
Example:
% Rotate the image by 45 degrees
rotated_img = imrotate(img, 45);
% Display the rotated image
imshow(rotated_img);
% Crop a region from the image
cropped_img = imcrop(img, [50 50 200 200]);
% Display the cropped image
imshow(cropped_img);
These core functions allow efficient image processing in MATLAB. They help streamline complex tasks with simple commands.
Advanced Techniques In Matlab
MATLAB offers powerful tools for image processing. These tools help in analyzing, enhancing, and segmenting images. Using these advanced techniques, users can achieve remarkable results. Let’s dive into some of the key techniques in MATLAB.
Edge Detection And Image Segmentation
Edge detection helps in identifying boundaries within images. MATLAB provides various methods for edge detection like the Sobel, Canny, and Prewitt methods. These techniques highlight the edges in an image effectively.
Image segmentation divides an image into parts. Each part represents different objects or regions. MATLAB’s image segmentation tools include thresholding, clustering, and region-based methods. These tools make it easy to isolate and analyze specific parts of an image.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Sobel | Detects edges using a gradient method. |
| Canny | Uses a multi-stage algorithm to detect edges. |
| Prewitt | Identifies edges similar to Sobel but less sensitive to noise. |
Image Enhancement And Noise Reduction
Image enhancement improves the visual quality of images. Techniques like histogram equalization and contrast adjustment are commonly used in MATLAB.
Noise reduction removes unwanted distortions from images. MATLAB offers filters like median, Gaussian, and Wiener to reduce noise. These filters help in improving the clarity of images.
- Histogram Equalization: Enhances contrast by adjusting the image’s intensity distribution.
- Contrast Adjustment: Modifies the brightness and contrast of an image.
- Median Filter: Reduces noise while preserving edges.
- Gaussian Filter: Smoothens images by averaging pixel values.
- Wiener Filter: Minimizes mean square error in images.
By utilizing these advanced techniques in MATLAB, users can achieve superior image processing results. Whether it’s edge detection, segmentation, enhancement, or noise reduction, MATLAB provides the necessary tools to excel.
Creative Projects Using Matlab
MATLAB is a powerful tool for creative image processing. You can create unique artworks. This section explores fun and artistic projects using MATLAB.
Designing Artistic Image Filters
Artistic image filters transform photos into stunning visuals. MATLAB makes designing these filters easy.
Here are some examples of artistic filters:
- Sepia Tone: Gives images a warm, antique look.
- Sketch Effect: Converts photos into pencil sketches.
- Oil Painting: Makes images look like oil paintings.
Below is a simple code snippet for a sepia filter:
function sepia_image = apply_sepia(image)
sepia_filter = [0.393, 0.769, 0.189;
0.349, 0.686, 0.168;
0.272, 0.534, 0.131];
sepia_image = imfilter(image, sepia_filter);
end
Use these filters to enhance your photo collection.
Creating Image Composites And Montages
Image composites blend several images into one. Montages display multiple images together.
These projects are useful for creating:
- Collages: Combine photos into a single image.
- Storyboards: Show a sequence of images to tell a story.
- Posters: Design posters with multiple images.
Here is an example of creating a simple montage:
images = {'image1.jpg', 'image2.jpg', 'image3.jpg'};
montage(images);
With these techniques, create impressive visual presentations.
Integrating Matlab With Other Software
MATLAB is a powerful tool for image processing. It becomes more powerful when integrated with other software. This integration allows users to leverage the strengths of multiple platforms. The result is a more comprehensive and efficient workflow.
Linking Matlab With Photoshop
Photoshop is a popular tool for image editing. By linking it with MATLAB, users can combine the best of both worlds. MATLAB can handle complex computations. Photoshop can provide advanced editing capabilities.
- Export images from MATLAB to Photoshop.
- Use MATLAB scripts to automate Photoshop tasks.
- Enhance images in Photoshop and analyze them in MATLAB.
Here is an example code snippet to export an image from MATLAB to Photoshop:
imwrite(image, 'myImage.jpg');
system('start photoshop myImage.jpg');
Using Matlab For 3d Image Processing
3D image processing is essential in many fields. MATLAB offers tools to handle 3D images with ease. These tools can create, manipulate, and analyze 3D images.
Here are some key features:
- Volume visualization
- 3D image segmentation
- Surface plotting
Below is a table highlighting the comparison between 2D and 3D image processing in MATLAB:
| Feature | 2D Image Processing | 3D Image Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Visualization | imshow | volshow |
| Segmentation | imbinarize | volseg |
| Plotting | imshow | surf |
Optimizing Performance In Matlab
Image processing in MATLAB can be resource-intensive. Proper optimization ensures faster and more efficient code execution. This section provides key practices to enhance performance in MATLAB.
Best Practices For Efficient Coding
Efficient coding can save both time and resources. Follow these best practices to improve your MATLAB code:
- Preallocate arrays: Always preallocate arrays to avoid dynamic resizing.
- Vectorize operations: Use vectorized operations instead of loops.
- Use built-in functions: MATLAB’s built-in functions are optimized for performance.
- Avoid using global variables: They slow down the execution and use more memory.
- Profile your code: Use MATLAB’s profiler to identify bottlenecks.
Here is an example of preallocating arrays:
n = 1000;
A = zeros(n,1); % Preallocating array
for i = 1:n
A(i) = i^2;
end
Leveraging Parallel Computing For Large Datasets
Working with large datasets can be challenging. Parallel computing can significantly speed up processing times.
To leverage parallel computing:
- Install the Parallel Computing Toolbox: This toolbox enables parallel processing.
- Use ‘parfor’ instead of ‘for’: The ‘parfor’ loop distributes iterations across multiple workers.
- Utilize ‘spmd’ blocks: They allow different parts of your code to run simultaneously.
- Use ‘gpuArray’: Offload computations to the GPU for faster processing.
Example of using ‘parfor’ loop:
parpool('local',4); % Create a pool of 4 workers
parfor i = 1:n
A(i) = i^2;
end
delete(gcp('nocreate')); % Close the pool
Parallel computing can dramatically reduce processing times, making your MATLAB code more efficient.
Case Studies And Real-world Applications
Image processing tools in MATLAB have revolutionized many industries and academic fields. From healthcare to automotive, the power of MATLAB in handling image data is unmatched. This section will explore real-world applications and case studies that highlight the innovative uses and research breakthroughs achieved using MATLAB.
Innovative Uses Of Matlab In The Industry
MATLAB is widely used in various industries for image processing tasks. Here are some notable applications:
- Healthcare: Doctors use MATLAB to analyze medical images. This helps in diagnosing diseases early.
- Automotive: Engineers use MATLAB for autonomous driving systems. It helps in detecting objects and lanes.
- Aerospace: MATLAB aids in satellite image analysis. It helps in monitoring weather and land changes.
- Manufacturing: Quality control teams use MATLAB to inspect products. It ensures defects are detected early.
Academic Research Breakthroughs Using Matlab
In academia, MATLAB plays a crucial role in image processing research. Several breakthroughs have been made possible with MATLAB:
- Brain Imaging: Researchers use MATLAB to study brain scans. This has led to new findings in neuroscience.
- Environmental Studies: MATLAB helps in analyzing environmental data. It aids in tracking climate change.
- Genomics: MATLAB is used to process genetic images. This has helped in understanding genetic disorders.
- Robotics: MATLAB assists in developing vision systems for robots. This has improved robot navigation.
These examples show how powerful MATLAB is in both industry and academia. The ability to process and analyze images effectively is crucial in many fields. MATLAB continues to be a leading tool for these tasks.
Credit: matlabsimulation.com
Future Of Image Processing With Matlab
The future of image processing is bright and innovative. MATLAB is leading this change with powerful tools. Professionals and students are excited about new possibilities. Below, we explore emerging trends and MATLAB’s evolving role.
Emerging Trends And Technologies
Many new technologies are shaping image processing. Here are a few key trends:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI helps in automating complex tasks. It makes image analysis faster and more accurate.
- Deep Learning: Deep learning models can recognize objects in images. This is useful in medical imaging and security systems.
- 3D Imaging: 3D imaging creates detailed models. It is useful in gaming, movies, and virtual reality.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing processes data closer to where it is created. This reduces latency and improves performance.
These trends are making image processing more efficient and powerful. They open new doors for innovation.
Matlab’s Evolving Role In Image Processing
MATLAB continues to evolve and adapt. It integrates these new technologies seamlessly. Here are some ways MATLAB is evolving:
- Enhanced Toolboxes: MATLAB offers toolboxes for deep learning and AI. These make it easy to implement advanced techniques.
- Interactive Apps: MATLAB apps allow users to visualize and process images interactively. This improves user experience and productivity.
- Integration with Hardware: MATLAB can interface with various hardware. This allows real-time image processing.
- Cloud Support: MATLAB supports cloud-based processing. This makes it scalable and accessible from anywhere.
These advancements make MATLAB a preferred choice for image processing. It continues to support innovation and creativity.
Matlab And Creativity
MATLAB is not just for technical tasks. It also fosters creativity. Artists and designers use MATLAB for visual effects. Here’s how:
| Field | Usage |
|---|---|
| Film and Animation | Creating special effects and animations. |
| Graphic Design | Designing intricate patterns and visuals. |
| Virtual Reality | Building immersive virtual environments. |
MATLAB offers tools to experiment and innovate. It bridges the gap between technology and art. This makes it unique and versatile.
As technologies evolve, MATLAB remains at the forefront. Its commitment to innovation and user experience is unmatched.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can You Do Image Processing In Matlab?
Yes, you can perform image processing in MATLAB. It offers extensive tools and functions for image analysis.
What Is The Image Tool In Matlab?
The image tool in MATLAB is a graphical user interface for displaying, analyzing, and processing images. It offers various functions for image manipulation, enhancement, and visualization.
How To Enable Image Processing Toolbox In Matlab?
Enable the Image Processing Toolbox in MATLAB by typing `license(‘test’, ‘Image_Toolbox’)` in the command window. Then, use `ver` to check installation.
What Is The Application Of Image Processing Toolbox Of Matlab?
The Image Processing Toolbox in MATLAB is used for image analysis, visualization, and algorithm development. It provides tools for image enhancement, filtering, transformation, and segmentation. Researchers and engineers use it to process medical images, satellite images, and more.
Conclusion
Mastering Matlab for image processing can greatly enhance your projects. This tool simplifies complex tasks, making analysis efficient. With its robust features, Matlab is essential for researchers and engineers. Dive into Matlab and unlock its potential to transform your image processing endeavors.
Start exploring today and elevate your work to new heights.



