Are you wondering if SQL is a business intelligence tool? You’re not alone.
If you work with data or want to unlock valuable insights for your business, understanding SQL’s role is crucial. While SQL itself isn’t a traditional BI tool that creates dashboards or visual reports, it’s the key that opens the door to your data.
You’ll discover how SQL powers business intelligence, why it matters to your decision-making, and how mastering it can boost your ability to analyze data like a pro. Keep reading to find out if SQL fits into your BI toolkit and how it can transform the way you handle business data.
Credit: www.todaysoftmag.com
Sql Basics
SQL plays a vital role in Business Intelligence (BI). It helps organizations collect and analyze data. BI relies on accurate data to make decisions. SQL provides the tools to access and transform this data. It is the backbone of many BI operations. Without SQL, handling large datasets would be difficult.
Data Querying And Extraction
SQL allows users to query databases quickly. Queries help find specific data from large tables. This process is essential for BI reports and dashboards. SQL commands like SELECT pull data based on conditions. Users can extract relevant information for analysis.
Data Manipulation And Aggregation
SQL supports data manipulation with commands like INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE. These actions keep data accurate and up-to-date. Aggregation functions such as SUM, AVG, and COUNT summarize data. Aggregated data reveals trends and patterns needed in BI.
Sql As Bi Foundation
SQL forms the foundation of many BI tools and platforms. It connects BI software to data stored in databases. SQL ensures data is consistent and ready for visualization. Many BI professionals rely on SQL skills daily. It bridges raw data and insightful business reports.
Role Of Sql In Bi
Comparing SQL with Business Intelligence (BI) tools reveals key differences in their roles and functions. Both are important in data management and analysis, but they serve distinct purposes. Understanding these differences helps businesses choose the right approach for their data needs.
Purpose Of Bi Tools
BI tools focus on turning raw data into meaningful insights. They help users explore data trends, create reports, and support decision-making. These tools are designed for business users who need easy access to data without deep technical skills.
SQL, on the other hand, is a language used to interact with databases. It retrieves and manipulates data stored in tables. SQL works behind the scenes to prepare data for analysis but does not provide built-in analysis or visualization features.
Visualization Vs Data Querying
BI tools offer rich visualizations like charts, graphs, and dashboards. These visuals make complex data easier to understand at a glance. Users can interact with data through drag-and-drop interfaces and filter options.
SQL is focused on querying data using commands. It returns rows of data based on specific criteria. SQL does not create visuals but provides the detailed data needed for BI tools to generate graphics.
Integration With Bi Platforms
Most BI platforms connect directly to SQL databases. They use SQL queries to extract data for reporting and analysis. This integration allows BI tools to leverage SQL’s power in managing large datasets.
While SQL handles the data extraction, BI tools handle data presentation and user interaction. Together, they form a complete system for business intelligence.
Comparing Sql With Bi Tools
SQL Server plays a vital role in business intelligence (BI). It offers tools for data storage, analysis, and reporting. Businesses use SQL Server to turn raw data into clear insights. This helps managers make informed decisions fast. SQL Server provides a strong platform to build BI solutions that fit different needs.
Sql Server Reporting Services
SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) allows creating and managing reports. Users can design reports with tables, charts, and images. Reports can be shared across the company easily. SSRS supports both paginated and interactive reports. It connects to many data sources, giving a full view of business data.
Analysis Services
SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) helps with data analysis and modeling. It builds multidimensional and tabular models for deep insights. SSAS supports complex calculations and data exploration. Users can slice and dice data to find trends. This service works well for forecasting and planning tasks.
Building Bi Solutions
Building BI solutions with SQL Server combines its different services. Data is stored in databases and cleaned for accuracy. Analysis Services processes data into meaningful models. Reporting Services shares results through customized reports. Together, these tools create a full BI system. This system supports data-driven decision-making in any business.

Credit: www.predictiveanalyticstoday.com
Sql Server And Bi
SQL plays a vital role in Business Intelligence (BI). It helps businesses collect, manage, and analyze data efficiently. Using SQL in BI brings many benefits that improve how data is handled and understood. These advantages make SQL a popular choice for BI professionals and data analysts.
Data Accuracy And Consistency
SQL ensures data accuracy by using clear rules for data entry and queries. It reduces errors by validating data before processing. Consistent data results from structured queries that follow the same logic every time. This reliability helps businesses make confident decisions based on trustworthy data.
Flexibility In Data Handling
SQL works well with various types of data and databases. It can handle large volumes of structured data quickly. Users can filter, sort, and join data from multiple sources easily. This flexibility allows teams to explore data from different angles and find useful insights fast.
Empowering Data Analysts
Data analysts gain control with SQL’s simple yet powerful commands. They can write queries to answer specific business questions. SQL enables them to create reports and dashboards without waiting for IT support. This independence speeds up analysis and improves productivity.
Benefits Of Using Sql In Bi
SQL is a powerful language for managing and querying data. Yet, it has limits as a business intelligence (BI) tool. Understanding these limits helps businesses choose the right tools for data analysis and reporting.
SQL works well with data retrieval and manipulation. But it lacks features that modern BI tools offer. These gaps can slow down data insights and decision-making.
Lack Of Visualization
SQL cannot create charts or graphs on its own. Visuals help users see trends and patterns quickly. Without visuals, users must export data to other software. This extra step adds time and complexity. It also limits how easily teams share insights.
Complexity For Non-technical Users
SQL requires knowledge of syntax and commands. Non-technical users often find it hard to write queries. Mistakes in queries can cause wrong results. This barrier reduces access to data insights. Business teams may depend on IT or analysts for reports.
Need For Complementary Tools
SQL works best with BI platforms and visualization tools. These tools build dashboards, reports, and interactive visuals. They also help with data cleaning and blending. Using only SQL means missing out on these benefits. Companies must invest in extra software for full BI capabilities.
Limitations Of Sql As Bi Tool
The future of SQL in business intelligence (BI) remains strong and promising. SQL continues to be a fundamental tool for querying and managing data. Its role expands as BI environments evolve with new technologies. Companies rely on SQL to extract insights and support decision-making. The language adapts to meet the growing needs of data analytics and reporting.
Evolving Sql Capabilities
SQL is becoming more powerful with new features. Advanced analytics functions help users perform complex calculations easily. Support for JSON and XML data types allows handling diverse data formats. Enhanced support for big data platforms improves scalability. These improvements keep SQL relevant for modern BI tasks.
Integration With Cloud Bi
Cloud-based BI platforms increasingly support SQL natively. SQL queries run directly on cloud data warehouses like Snowflake and BigQuery. This reduces data movement and speeds up analysis. Cloud integration enables real-time data access and collaboration. SQL’s compatibility with cloud tools drives its widespread adoption.
Role In Data Analytics Trends
SQL aligns well with current data analytics trends. It works smoothly with machine learning models and AI tools. SQL enables quick data preparation for predictive analytics. The language supports automation of repetitive data tasks. Its simplicity helps non-technical users explore data and create reports.
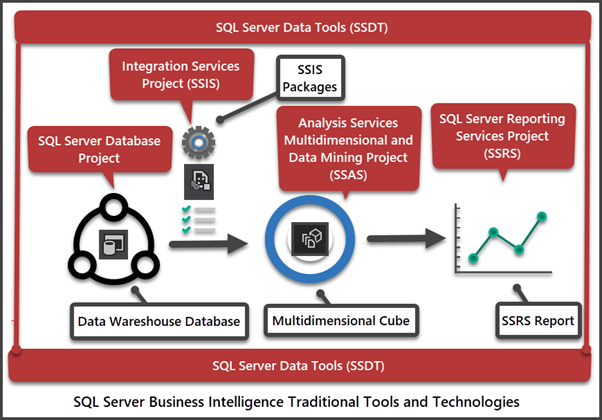
Credit: codingsight.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Sql Business Intelligence?
SQL is not a business intelligence tool but a language used to query and manage data within BI systems. It supports data analysis and reporting.
What Type Of Tool Is Sql?
SQL is a standard language used to create, manage, and manipulate relational databases. It enables efficient data querying and analysis.
Which Tool Is Widely Used For Business Intelligence?
Microsoft Power BI is widely used for business intelligence due to its powerful data visualization and analytics features.
Are Sql And Db The Same?
SQL is a language used to manage and query databases. A database (DB) stores data, while SQL interacts with that data. They are related but not the same.
Conclusion
SQL plays a key role in business intelligence tasks. It helps users access and analyze data quickly. While SQL itself is not a BI tool, it supports many BI platforms. Business intelligence tools often use SQL to gather insights. Learning SQL boosts your ability to work with data.
Understanding SQL basics can improve decision-making in business. Combining SQL with BI tools creates powerful data solutions. The right skills and tools together drive smart business actions.