Matlab Image Processing Tool is a powerful platform for analyzing and processing images. It offers a wide range of functions and algorithms.
Matlab’s Image Processing Tool provides engineers and researchers with advanced image analysis capabilities. This tool supports tasks like image enhancement, noise reduction, segmentation, and feature extraction. Users can develop and implement custom algorithms using Matlab’s extensive library of functions. The graphical user interface (GUI) simplifies workflow, making it easy for users to visualize and manipulate images.
Matlab’s compatibility with various file formats ensures seamless integration into different projects. Its robust performance and flexibility make it a preferred choice for professionals in fields like medical imaging, computer vision, and remote sensing.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Introduction To Matlab Image Processing
Matlab is a powerful tool for image processing. It helps in manipulating and enhancing images. This makes it essential for many fields. Let’s explore the power and scope of Matlab.
The Power Of Matlab For Visual Enhancement
Matlab provides many functions for image enhancement. These functions can improve image quality. You can adjust brightness, contrast, and colors with ease.
- Brightness Adjustment
- Contrast Enhancement
- Color Correction
Here is a simple code example:
img = imread('image.jpg');
bright_img = imadjust(img, [0.3 0.7], []);
imshow(bright_img);
This code adjusts the brightness of an image. Matlab makes such tasks simple and quick.
Scope Of Image Processing With Matlab
The scope of image processing with Matlab is vast. It includes many applications:
- Medical Imaging
- Remote Sensing
- Computer Vision
In medical imaging, Matlab helps analyze X-rays and MRIs. It can detect and highlight abnormalities. This helps doctors in diagnosis.
For remote sensing, Matlab processes satellite images. It can identify land use patterns and changes.
In computer vision, Matlab supports object detection. It can recognize faces and detect motion.
| Application | Use |
|---|---|
| Medical Imaging | Analyze X-rays, MRIs |
| Remote Sensing | Process satellite images |
| Computer Vision | Object detection, face recognition |
Matlab makes image processing tasks easier and more efficient. It offers tools and functions for many applications.
Core Features Of Matlab For Image Processing
Matlab stands out as a leading tool for image processing. It offers a range of powerful features. These features make complex tasks simple and efficient. Let’s explore some core features of Matlab for image processing.
Interactive Tools And User Interface
Matlab provides a user-friendly interface. It includes interactive tools for easy image manipulation. Users can quickly adjust image parameters. The drag-and-drop feature makes it simple to use. The interactive environment helps in visualizing data effectively.
- Image Viewer: View and zoom into images with ease.
- ROI Tools: Define regions of interest easily.
- Histogram Display: Visualize image intensity distributions.
The interface supports live editing and visualization. Users can see changes in real-time. This feature saves time and enhances productivity. The UI is designed for both beginners and experts.
Advanced Algorithms And Functions
Matlab includes a rich set of advanced algorithms. These algorithms help in various image processing tasks. They are optimized for performance and accuracy. Users can apply these functions effortlessly.
| Algorithm | Description |
|---|---|
| Edge Detection | Finds edges in images using methods like Canny and Sobel. |
| Image Segmentation | Divides images into meaningful segments. |
| Morphological Operations | Processes images based on shapes. |
Matlab’s functions are comprehensive and powerful. They cover a wide range of image processing needs. Users can perform tasks like filtering, transformation, and enhancement. These functions are well-documented and easy to implement.
Getting Started With Matlab’s Image Processing Toolbox
Matlab’s Image Processing Toolbox is an essential tool for image analysis. It helps professionals and hobbyists alike. This section will guide you through the basics.
Installation And Setup
First, ensure you have Matlab installed. If not, download it from the MathWorks official site. Follow the installation steps provided.
Once Matlab is installed, you need to install the Image Processing Toolbox. Open Matlab and navigate to the Add-Ons button in the environment toolbar. Search for “Image Processing Toolbox” and click Install.
After installation, verify it by typing the following command in the command window:
verIf installed correctly, you should see Image Processing Toolbox listed.
Navigation Of Basic Toolbox Functions
Familiarize yourself with the basic functions of the toolbox. Here are some key functions:
- imread: Reads an image file.
- imshow: Displays an image.
- imwrite: Writes an image to a file.
- rgb2gray: Converts an RGB image to grayscale.
- imresize: Resizes an image.
Below is a simple example code to read and display an image:
% Read an image
img = imread('your_image.jpg');
% Display the image
imshow(img);
Let’s break down the code:
- The imread function reads the image file.
- The imshow function displays the image.
These basic commands allow you to handle images in Matlab. Experiment with different images to get comfortable. This will build your confidence with the toolbox.
Next, try converting an image to grayscale:
% Convert the image to grayscale
gray_img = rgb2gray(img);
% Display the grayscale image
imshow(gray_img);
This code converts an RGB image to grayscale and displays it. Play around with these functions to explore their capabilities further.
Fundamentals Of Image Manipulation
Matlab is a powerful tool for image processing. Understanding the fundamentals of image manipulation is crucial. This section covers the basic steps involved in handling images in Matlab.
Reading And Displaying Images
First, you need to read an image into Matlab. Use the imread function:
img = imread('image.jpg');Once the image is read, display it using the imshow function:
imshow(img);These simple steps help you load and view images.
Image Conversion And Scaling
Sometimes, you need to convert images to different formats. Use the im2gray function to convert an image to grayscale:
gray_img = im2gray(img);Displaying the grayscale image is also simple:
imshow(gray_img);Scaling images is another important task. Use the imresize function to resize an image:
resized_img = imresize(img, [100, 100]);Now, let’s display the resized image:
imshow(resized_img);These basic operations form the core of image manipulation in Matlab.
Advanced Image Enhancement Techniques
Matlab Image Processing Tool offers powerful capabilities for image enhancement. These techniques improve image quality for various applications. This section covers advanced methods to enhance images effectively.
Noise Reduction And Filtering
Noise reduction is crucial for clear images. Matlab provides several filters to reduce noise. Common filters include:
- Median Filter: Removes salt-and-pepper noise.
- Gaussian Filter: Reduces Gaussian noise.
- Wiener Filter: Adapts to local image variance.
Use these filters to clean images before further processing. Here’s a simple example using a Median Filter in Matlab:
I = imread('noisy_image.jpg');
filtered_image = medfilt2(I);
imshow(filtered_image);
Spatial Transformation And Morphological Operations
Spatial transformations modify image geometry. Morphological operations process image shapes. These techniques include:
| Transformation | Description |
|---|---|
| Translation | Moves the image in x or y direction. |
| Rotation | Rotates the image by a specified angle. |
| Scaling | Changes the image size proportionally. |
Morphological operations enhance image structures. Common operations include:
- Dilation: Expands image regions.
- Erosion: Shrinks image regions.
- Opening: Removes small objects from the image.
- Closing: Fills small holes in the image.
Here is an example of performing Dilation in Matlab:
SE = strel('disk', 5);
dilated_image = imdilate(I, SE);
imshow(dilated_image);
Credit: www.researchgate.net
Color Processing And Analysis
Color processing and analysis are essential in many image processing applications. It helps in object identification, image enhancement, and pattern recognition. Matlab provides robust tools for color processing, making it simpler to manipulate and analyze images.
Color Space Transformation
Color space transformation is a crucial step in image processing. It converts images from one color space to another. Common color spaces include RGB, HSV, and YCbCr. Each color space has its unique advantages.
For example, the RGB color space is used for display screens. The HSV color space is useful for color segmentation. The YCbCr color space is often used in video compression.
Here is a Matlab code snippet for converting an RGB image to HSV:
rgbImage = imread('image.jpg');
hsvImage = rgb2hsv(rgbImage);
imshow(hsvImage);Color-based Segmentation And Tracking
Color-based segmentation separates objects in an image based on color. This is useful for identifying and tracking objects. Matlab provides functions like imbinarize and bwlabel to assist in segmentation.
For example, to segment a red object in an image:
rgbImage = imread('image.jpg');
redChannel = rgbImage(:,:,1);
binaryImage = imbinarize(redChannel);
labeledImage = bwlabel(binaryImage);
imshow(label2rgb(labeledImage));Tracking moving objects can be achieved by analyzing consecutive frames. Matlab’s vision.ForegroundDetector can detect moving objects based on color:
foregroundDetector = vision.ForegroundDetector();
videoReader = VideoReader('video.mp4');
while hasFrame(videoReader)
frame = readFrame(videoReader);
foreground = step(foregroundDetector, frame);
imshow(foreground);
endBy combining color-based segmentation and tracking, you can create powerful image analysis tools.
Edge Detection And Feature Extraction
Edge detection is crucial in image processing. It helps in identifying object boundaries. Feature extraction is another key aspect. It involves detecting important parts of an image. Matlab offers powerful tools for both tasks.
Gradient Methods And Contour Finding
Gradient methods detect edges by measuring intensity changes. The Sobel and Prewitt operators are popular choices. They calculate the gradient at each pixel.
Contour finding goes a step further. It traces the edges to form continuous lines. Matlab’s `edge` function is often used. Here’s a simple code example:
img = imread('image.jpg');
edges = edge(rgb2gray(img), 'Sobel');
imshow(edges);
Texture Analysis And Shape Descriptors
Texture analysis examines patterns in an image. It identifies repetitive features. Matlab’s `graycomatrix` function is useful for this. It creates a matrix of pixel intensity relationships.
Shape descriptors provide information about object shapes. They help in recognizing and classifying objects. Common descriptors include area, perimeter, and eccentricity. The `regionprops` function in Matlab extracts these features. Here’s a sample code:
img = imread('image.jpg');
bw = imbinarize(rgb2gray(img));
stats = regionprops(bw, 'Area', 'Perimeter', 'Eccentricity');
disp(stats);
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Gradient Methods | Detect edges based on intensity changes. |
| Contour Finding | Trace edges to form continuous lines. |
| Texture Analysis | Examines repetitive patterns in the image. |
| Shape Descriptors | Provide details about object shapes. |
Real-world Applications And Case Studies
MATLAB’s Image Processing Tool is a powerful tool for various industries. It helps solve real-world problems. Let’s explore some key applications and case studies.
Medical Imaging And Diagnostics
In medical imaging, MATLAB enhances image quality. It helps doctors detect diseases early. Some real-world cases include:
- CT Scan Analysis: MATLAB improves the clarity of CT scans. It helps doctors spot tiny tumors.
- MRI Processing: It sharpens MRI images, highlighting critical areas. This aids in accurate diagnosis.
- Ultrasound Imaging: MATLAB filters noise from ultrasound images. This provides clearer images for fetal health checks.
Industrial Quality Control And Automation
MATLAB is vital in industrial quality control. It automates inspection processes, ensuring high standards. Key applications include:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Defect Detection | MATLAB identifies flaws in products. It ensures only high-quality items reach customers. |
| Robot Vision | It guides robots in assembly lines. This boosts efficiency and accuracy. |
| Surface Inspection | MATLAB examines surfaces for imperfections. It helps maintain product quality. |
Tips And Best Practices
Matlab Image Processing Tool is a powerful resource for image analysis. Knowing the best tips and practices can enhance your workflow. This guide will help optimize performance and ensure your code remains maintainable.
Optimizing Performance
Optimizing performance is crucial for handling large images or datasets. Here are some tips to ensure Matlab runs efficiently:
- Preallocate arrays: Always preallocate arrays to avoid dynamically resizing them. This reduces computation time.
- Use built-in functions: Matlab’s built-in functions are optimized for performance. Use them whenever possible instead of writing custom code.
- Vectorize your code: Replace loops with vectorized code to speed up execution.
- Profile your code: Use the
profilefunction to identify bottlenecks in your code.
Writing Maintainable Code
Writing maintainable code ensures that your projects are easy to update and debug. Consider these best practices:
- Comment your code: Write clear comments to explain the purpose of each section.
- Use meaningful variable names: Choose descriptive names for variables and functions.
- Modularize your code: Break your code into functions and scripts to make it more readable.
- Consistent formatting: Stick to a consistent code style. This includes indentation and spacing.
Following these tips will help you get the most out of Matlab Image Processing Tool.
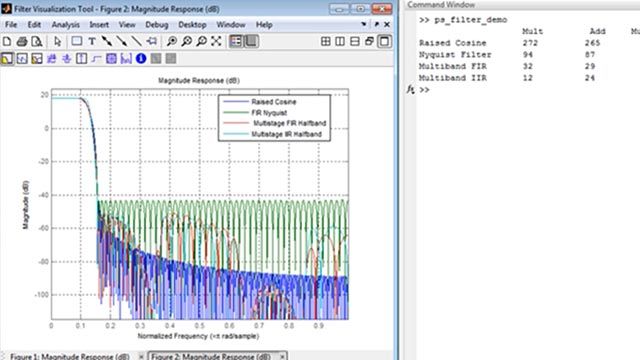
Credit: www.mathworks.com
Future Trends In Matlab Image Processing
Matlab Image Processing is evolving rapidly. With new advancements, it is becoming more powerful. Let’s explore the future trends shaping this tool.
Integration With Ai And Machine Learning
Matlab is integrating with AI and Machine Learning. This fusion enhances image analysis. AI algorithms help in detecting patterns. Machine Learning improves accuracy over time.
Imagine a system that learns from data. Matlab makes this possible. It offers pre-trained models. You can also train your own models. This flexibility is key to advanced processing.
Here is a simple example of code integration:
% Load pre-trained model
net = alexnet;
% Read and process an image
img = imread('image.jpg');
img = imresize(img, [227 227]);
% Classify the image
label = classify(net, img);
disp(label);
Emerging Features And Updates
Matlab continuously updates its features. Each update brings more capabilities. Let’s look at some emerging features:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Deep Learning Toolbox | Enhanced neural network design and training |
| GPU Acceleration | Faster processing with parallel computing |
| Interactive Apps | User-friendly interfaces for complex tasks |
These features simplify complex tasks. They offer more control and precision. Matlab’s user community also contributes to its growth. This collaborative environment fosters innovation.
New updates also focus on usability. They aim to improve the user experience. Enhanced documentation and tutorials make it accessible. Even beginners can quickly get started.
In summary, Matlab Image Processing is evolving. Its integration with AI and new features are groundbreaking. These trends make it a powerful tool for image analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can You Do Image Processing In Matlab?
Yes, MATLAB can perform image processing. Use built-in functions and toolboxes for tasks like filtering, segmentation, and transformation.
What Is The Image Processing Toolbox In Matlab?
The image processing toolbox in MATLAB offers algorithms, functions, and apps for image analysis, visualization, and algorithm development. It supports tasks like image enhancement, filtering, and geometric transformations.
What Is The Alternative To Matlab Image Processing?
An alternative to MATLAB for image processing is Python with libraries like OpenCV, scikit-image, and PIL. These tools are powerful, free, and widely used.
Which Is Better For Image Processing Matlab Or Python?
Python is better for image processing due to its extensive libraries like OpenCV and user-friendly syntax. MATLAB is powerful but more expensive.
Conclusion
The Matlab Image Processing Tool offers incredible features for image analysis and enhancement. Its powerful algorithms simplify complex tasks. Whether you’re a beginner or expert, Matlab provides tools to elevate your projects. Explore its capabilities to improve your image processing workflow and achieve outstanding results.
Unlock the potential of your images with Matlab today.