Matlab provides essential tools for simple image processing tasks. These tools enable users to analyze, manipulate, and enhance images efficiently.
Matlab’s image processing toolbox offers a comprehensive suite of functions for image analysis and enhancement. Users can perform tasks like filtering, edge detection, and morphological operations with ease. The toolbox also includes tools for geometric transformations and image registration, making it versatile for various applications.
Matlab’s user-friendly interface and robust documentation help beginners and professionals alike. Its integration with other Matlab toolboxes further expands its capabilities. With Matlab, users can quickly prototype and test image processing algorithms, speeding up development and research. This makes Matlab an invaluable tool for engineers, researchers, and anyone working with digital images.
Credit: www.mathworks.com
Introduction To Matlab Image Processing
MATLAB is a powerful tool for image processing. It helps analyze and modify images with ease. This makes it popular among researchers and engineers.
The Role Of Matlab In Image Analysis
MATLAB plays a crucial role in image analysis. It offers various functions to process images. You can filter, enhance, and segment images effectively. The Image Processing Toolbox in MATLAB has built-in algorithms. These algorithms simplify complex tasks.
MATLAB can handle large sets of image data. It can also automate repetitive image processing tasks. This saves time and reduces manual effort. MATLAB supports different image formats. It can read, write, and display images effortlessly.
Key Features Of Matlab’s Image Processing Toolbox
The Image Processing Toolbox in MATLAB has many features. These features make image processing easy and efficient.
- Image Enhancement: Improve the quality of images.
- Image Segmentation: Divide images into meaningful parts.
- Noise Reduction: Remove unwanted noise from images.
- Geometric Transformations: Rotate, scale, and resize images.
- Feature Extraction: Identify important features in images.
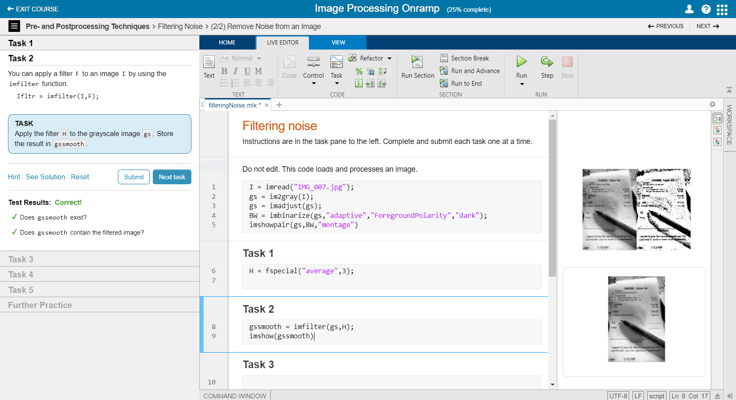
Here is a simple example of image enhancement using MATLAB:
% Read an image
img = imread('example.jpg');
% Convert to grayscale
grayImg = rgb2gray(img);
% Enhance the image
enhancedImg = imadjust(grayImg);
% Display the original and enhanced images
imshowpair(grayImg, enhancedImg, 'montage');
This code reads an image and converts it to grayscale. Then, it enhances the image using the imadjust function. Finally, it displays the original and enhanced images side by side.
MATLAB’s Image Processing Toolbox makes tasks simpler. Its features help achieve better results quickly. This is why many users prefer MATLAB for image processing tasks.

Credit: www.mathworks.com
Getting Started With Basic Functions
MATLAB offers a variety of tools for image processing. Starting with basic functions is essential for beginners. This guide will help you understand how to import and display images using MATLAB’s simple image processing tools.
Importing Images Into Matlab
Importing images into MATLAB is straightforward. Use the imread function to load an image. This function reads an image from a file and stores it in an array.
Here’s a simple example:
img = imread('example.jpg');
imread supports multiple file formats like JPEG, PNG, and TIFF. The function reads the image file and assigns it to the variable img. Make sure the file path is correct.
Displaying Images And Understanding Formats
Displaying images in MATLAB is easy. Use the imshow function to visualize the image. This function displays the image stored in the array.
Example usage:
imshow(img);
The imshow function opens a new figure window and displays the image. This helps you inspect the image visually.
MATLAB supports various image formats. Common formats include:
- JPEG (.jpg, .jpeg)
- PNG (.png)
- TIFF (.tif, .tiff)
Each format has its own advantages. Choose the format based on your requirements. For example, JPEG is good for photographs, while PNG supports transparency.
Understanding these formats helps in selecting the right one for your needs. Use the imfinfo function to get detailed information about an image file:
info = imfinfo('example.jpg');
The imfinfo function returns a structure containing information like file size, image dimensions, and format type.
Here’s a table summarizing some common image formats and their uses:
| Format | File Extension | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| JPEG | .jpg, .jpeg | Photographs |
| PNG | .png | Graphics with transparency |
| TIFF | .tif, .tiff | High-quality images |
By understanding these basics, you can start working with images in MATLAB effectively. Practice these functions to gain confidence in image processing.
Image Enhancement Techniques
Image enhancement techniques improve the quality of images. These methods help to bring out hidden details in images. MATLAB provides various tools for image enhancement. This section focuses on some of these techniques.
Contrast Adjustment And Histogram Equalization
Contrast adjustment is crucial for better image visibility. Low contrast images appear dull and lack detail. MATLAB allows you to adjust contrast using simple commands. You can use the imadjust function to enhance contrast.
Histogram equalization is another powerful technique. It spreads out the most frequent intensity values. This makes the image clearer and more detailed. Use the histeq function for histogram equalization.
Here is a simple example of both techniques:
% Read an image
I = imread('image.jpg');
% Adjust contrast
adjusted = imadjust(I);
% Histogram equalization
equalized = histeq(I);
% Display results
subplot(1,3,1), imshow(I), title('Original');
subplot(1,3,2), imshow(adjusted), title('Contrast Adjusted');
subplot(1,3,3), imshow(equalized), title('Histogram Equalized');
Noise Reduction And Filtering Methods
Noise reduction is essential for clear images. Images often contain unwanted noise. MATLAB offers various filtering methods to reduce noise. Common methods include median and Gaussian filtering.
Median filtering is effective for salt-and-pepper noise. It replaces each pixel value with the median of neighboring pixels. Use the medfilt2 function to apply median filtering.
Gaussian filtering is useful for reducing Gaussian noise. It smooths the image by averaging the pixels. Use the imgaussfilt function for Gaussian filtering.
Here is an example of applying these filters:
% Read a noisy image
I = imread('noisy_image.jpg');
% Apply median filter
medianFiltered = medfilt2(I);
% Apply Gaussian filter
gaussianFiltered = imgaussfilt(I, 2);
% Display results
subplot(1,3,1), imshow(I), title('Noisy');
subplot(1,3,2), imshow(medianFiltered), title('Median Filtered');
subplot(1,3,3), imshow(gaussianFiltered), title('Gaussian Filtered');
These techniques help to improve image quality significantly. They make images more suitable for analysis and interpretation.
Color Image Processing
Matlab offers powerful tools for color image processing. These tools help you manipulate, analyze, and transform color images with ease. By understanding these tools, you can enhance your images and extract valuable information.
Working With Rgb Channels
Color images are usually represented in the RGB color space. RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue. Each color image can be split into three separate channels:
- Red Channel: Contains the red component of the image.
- Green Channel: Contains the green component of the image.
- Blue Channel: Contains the blue component of the image.
In Matlab, you can easily separate these channels. Here’s a simple example:
% Read an image
image = imread('image.jpg');
% Separate RGB channels
redChannel = image(:,:,1);
greenChannel = image(:,:,2);
blueChannel = image(:,:,3);
% Display each channel
figure, imshow(redChannel), title('Red Channel');
figure, imshow(greenChannel), title('Green Channel');
figure, imshow(blueChannel), title('Blue Channel');
Color Transformation And Color Space Conversion
Color transformations are essential in image processing. They help change the representation of colors in an image. Matlab supports various color space conversions:
- RGB to Grayscale: Converts color images to shades of gray.
- RGB to HSV: Converts RGB images to Hue, Saturation, and Value.
- RGB to YCbCr: Converts RGB images to Luminance and Chrominance.
Here’s an example of converting an RGB image to grayscale:
% Read an image
image = imread('image.jpg');
% Convert RGB to Grayscale
grayImage = rgb2gray(image);
% Display the grayscale image
figure, imshow(grayImage), title('Grayscale Image');
Color transformations can also enhance image analysis. By converting to different color spaces, you can isolate features more effectively. Use Matlab’s built-in functions to achieve accurate and efficient results.
Morphological Operations
Morphological operations are essential tools in image processing. They help analyze and process shapes within an image. These operations are based on structuring elements. They modify the geometric structure of objects in an image.
Understanding Structuring Elements
Structuring elements are small matrices used in morphological operations. They define the neighborhood of a pixel. Common shapes include square, rectangle, and disk. These elements probe the input image.
Here’s a simple table to understand structuring elements:
| Shape | Description |
|---|---|
| Square | All pixels within a square neighborhood. |
| Rectangle | All pixels within a rectangular neighborhood. |
| Disk | All pixels within a circular neighborhood. |
Erosion And Dilation For Shape Analysis
Erosion and dilation are basic morphological operations. Erosion shrinks objects. Dilation expands objects.
Erosion uses a structuring element to remove pixels on object boundaries. It helps in removing small noise. Here’s a simple MATLAB code for erosion:
se = strel('disk', 5);
erodedImage = imerode(originalImage, se);
Dilation adds pixels to the boundaries of objects. It helps in filling small holes. Here’s a simple MATLAB code for dilation:
se = strel('disk', 5);
dilatedImage = imdilate(originalImage, se);
Both operations are crucial for shape analysis. They help in extracting meaningful features. Use them to enhance image processing tasks.
Edge Detection And Image Segmentation
Edge detection and image segmentation are key tools in image processing. These techniques help identify objects and boundaries in images. Matlab offers simple yet powerful tools for these tasks.
Implementing Edge Detection Filters
Edge detection filters help find the edges in an image. Matlab provides many filters for this purpose.
- Sobel filter: This filter detects edges by calculating gradient magnitude.
- Prewitt filter: Similar to Sobel but uses a different kernel.
- Canny filter: This filter is more complex but gives better edge detection.
Here is a simple code example to use the Sobel filter in Matlab:
img = imread('example.jpg');
grayImg = rgb2gray(img);
edges = edge(grayImg, 'Sobel');
imshow(edges);
Segmentation Techniques For Object Recognition
Image segmentation divides an image into parts. Each part represents an object or region.
Matlab offers several segmentation techniques:
- Thresholding: This method separates objects based on pixel values.
- Region-based segmentation: This method groups pixels into regions.
- Clustering: This method uses algorithms like k-means to segment images.
Here’s how to perform thresholding in Matlab:
img = imread('example.jpg');
grayImg = rgb2gray(img);
thresholdValue = graythresh(grayImg);
binaryImg = imbinarize(grayImg, thresholdValue);
imshow(binaryImg);
Using these tools, you can easily perform edge detection and image segmentation in Matlab. These techniques are essential for advanced image analysis and object recognition tasks.
Feature Extraction And Analysis
Feature extraction is crucial for image processing tasks. It helps identify important parts of an image. Matlab offers tools to make this easy and efficient. Let’s explore how Matlab can help extract and analyze image features.
Identifying And Extracting Features
Matlab provides various functions to identify and extract features. These features can be edges, corners, or objects within the image.
- Edge Detection: Use
edge()function to find edges in an image. - Corner Detection: Use
detectHarrisFeatures()to find corners. - Object Detection: Use
regionprops()to detect objects.
Here is an example code to detect edges:
img = imread('image.jpg');
edges = edge(rgb2gray(img), 'Canny');
imshow(edges);
Quantitative Analysis Of Image Features
Once features are extracted, quantitative analysis helps measure their properties. Matlab provides tools to measure these properties accurately.
| Feature | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Area | regionprops() | Measures the area of objects. |
| Perimeter | regionprops() | Calculates the perimeter of objects. |
| Centroid | regionprops() | Finds the center point of objects. |
Example code for calculating the area of objects:
img = imread('image.jpg');
bw = imbinarize(rgb2gray(img));
stats = regionprops(bw, 'Area');
disp([stats.Area]);
Advanced Applications And Automation
MATLAB offers powerful tools for image processing. This can help with advanced applications and automation. These tools make complex tasks simple. They also save time by automating repetitive processes.
Automating Tasks With Scripting
MATLAB scripting can automate many image processing tasks. This includes reading, modifying, and saving images. The scripts can handle large batches of images at once. Here is an example of a simple script:
% Read an image
image = imread('sample.jpg');
% Convert the image to grayscale
grayImage = rgb2gray(image);
% Save the processed image
imwrite(grayImage, 'gray_sample.jpg');
This script reads an image, converts it to grayscale, and saves it. You can also add more steps for advanced processing.
Case Studies: Real-world Applications Of Matlab Image Processing
In medical imaging, MATLAB helps in analyzing X-rays and MRI scans. Doctors use it to detect diseases early. It improves accuracy and speeds up diagnosis.
Factories use MATLAB for quality control. It checks products for defects automatically. This improves efficiency and reduces human error.
Scientists use MATLAB to analyze satellite images. They track weather patterns and changes in the environment. This helps in predicting natural disasters.
| Application | Industry | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Imaging | Healthcare | Early disease detection |
| Quality Control | Manufacturing | Improves efficiency |
| Satellite Analysis | Environmental Science | Predicts natural disasters |
These examples show the power of MATLAB in real-world applications. It simplifies complex tasks and makes processes more efficient.
Integrating With Other Tools And Languages
MATLAB is a powerful tool for image processing. It also integrates well with other tools and languages. This makes it very versatile. You can enhance its functionality by linking it with other programs. Let’s explore how to integrate MATLAB with different tools.
Interfacing Matlab With Other Programming Languages
MATLAB can interface with many programming languages. These include Python, C/C++, Java, and .NET. This allows you to use the strengths of each language. For example, you can call Python scripts directly from MATLAB. This is done using the pyrun function.
Using C/C++ in MATLAB is also simple. You can create MEX files. These are C/C++ programs that run in MATLAB. They help speed up computations. Java integration is also possible. You can use Java classes and methods directly in MATLAB.
| Language | Integration Method |
|---|---|
| Python | pyrun, pyenv |
| C/C++ | MEX files, shared libraries |
| Java | Java classes, methods |
| .NET | .NET assemblies, methods |
Leveraging Matlab’s Capabilities With External Libraries
MATLAB can use external libraries to boost its capabilities. Libraries like OpenCV and FFmpeg are very popular. They offer advanced image processing features. You can use these libraries directly from MATLAB.
Using OpenCV in MATLAB is straightforward. First, install the library. Then, call its functions from MATLAB. This allows you to perform complex image operations. FFmpeg is another great library. It helps with video processing. You can convert, edit, and filter videos using FFmpeg functions.
- OpenCV: For advanced image processing
- FFmpeg: For video processing tasks
Integrating these libraries with MATLAB enhances its functionality. This makes MATLAB a more powerful tool for image processing tasks.
Conclusion And Future Directions
MATLAB offers simple tools for image processing. These tools help in analyzing and enhancing images. Let’s summarize the key points and explore future trends.
Summarizing Key Takeaways
- Ease of Use: MATLAB’s tools are user-friendly.
- Versatility: The tools can handle various image types.
- Functionality: MATLAB includes many functions for image processing.
- Speed: The tools process images quickly.
- Integration: MATLAB works well with other software.
Emerging Trends In Image Processing With Matlab
New trends are shaping the future of image processing with MATLAB. These trends are advancing the field.
- Machine Learning Integration: MATLAB now includes machine learning for better image analysis.
- Real-Time Processing: Real-time image processing is becoming possible with MATLAB.
- Cloud Computing: MATLAB supports cloud computing for large-scale image processing.
- Enhanced Visualization: New tools are improving image visualization in MATLAB.
- Automated Tools: MATLAB is developing more automated image processing tools.
MATLAB’s simple image processing tools are powerful. They continue to evolve with new trends and technologies. These advancements make MATLAB a top choice for image processing.

Credit: simulation4vehicle.blogspot.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How To Use Matlab For Image Processing For Beginners?
Begin by installing MATLAB and the Image Processing Toolbox. Import your image using `imread()`. Use functions like `imshow()`, `imadjust()`, and `edge()` for basic processing tasks. Save results with `imwrite()`. Follow MATLAB documentation for detailed tutorials.
What Matlab Software Is Used For Image Processing?
MATLAB software used for image processing includes the Image Processing Toolbox. This toolbox provides functions for image analysis, visualization, and algorithm development.
What Is The Image Processing Toolbox In Matlab?
The Image Processing Toolbox in MATLAB provides tools for image analysis, visualization, and algorithm development. It includes functions for filtering, transforming, and segmenting images. This toolbox is essential for tasks like object detection, feature extraction, and image enhancement. It supports various image formats and offers interactive apps for streamlined workflows.
What Is The Alternative To Matlab Image Processing?
An alternative to MATLAB for image processing is Python with libraries like OpenCV, PIL, and scikit-image. These tools offer powerful and flexible image processing capabilities.
Conclusion
Mastering Matlab’s image processing tools can greatly enhance your projects. These simple tools offer robust features for beginners and experts. Start experimenting today to unlock their full potential. You’ll find that improving your image processing skills is both rewarding and beneficial.
Explore Matlab and take your work to the next level.