Are you ready to boost your online presence with a stunning landing page? Designing a landing page with CSS can be a game-changer for your website, helping you capture leads, promote products, or share important information.
But where do you start? You might feel overwhelmed by the technical jargon and endless options, but don’t worry—you’re not alone. Imagine the satisfaction of crafting a page that not only looks great but also converts visitors into loyal followers.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through every step, breaking down complex concepts into simple actions. You’ll discover tips and tricks to make your landing page not just visually appealing but also highly functional. Stay with us, and let’s transform your ideas into reality. Keep reading to unlock the secrets of creating a CSS landing page that truly works for you!
Understanding Landing Pages
Landing pages help catch a visitor’s attention right away. They aim to turn visitors into customers. The main goal is to have a clear message. This message must be easy to understand. A strong landing page tells users what to do next. This could be signing up for a newsletter or buying a product. Every element should focus on one single goal. This makes the page effective and simple.
A landing page needs a few key elements. First, a strong headline grabs attention. Next, clear images help tell your story. Text should be short and simple. A call-to-action button tells users what to do. This could be “Buy Now” or “Learn More”. Trust signals, like reviews, build confidence. These elements together make a landing page effective.
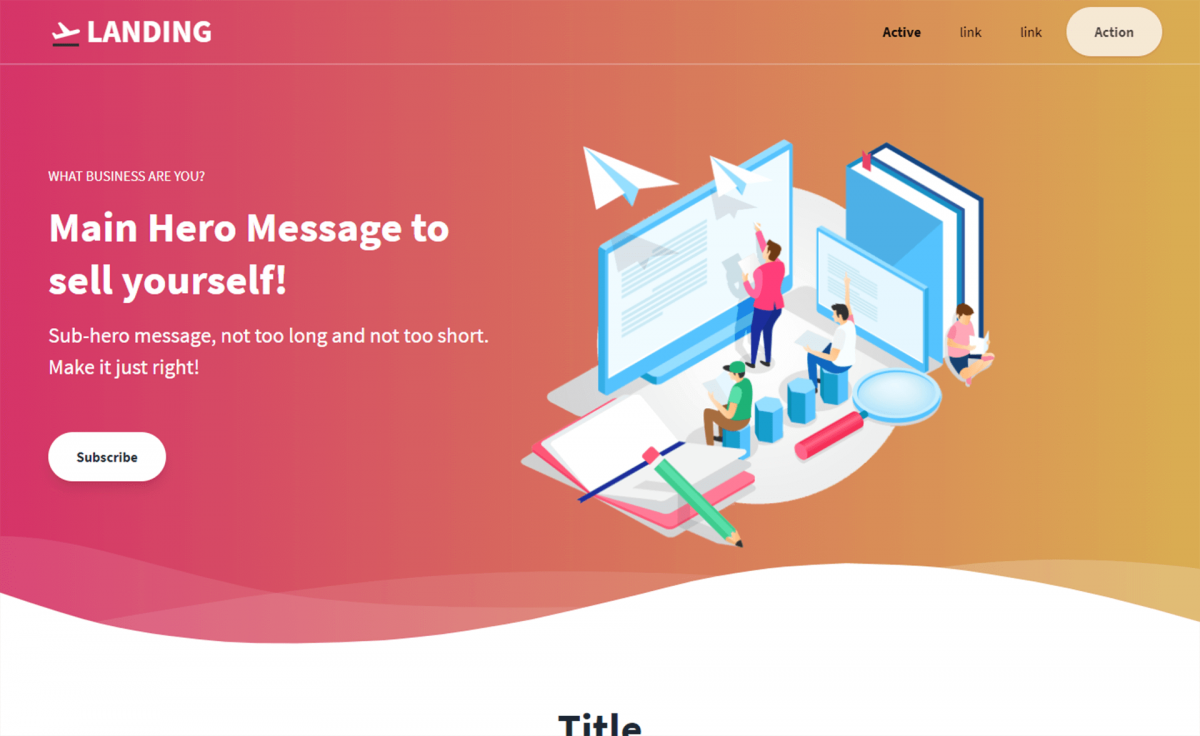
Credit: themewagon.com
Essential Css Concepts
CSS begins with selectors. Selectors pick elements to style. Use properties to describe how elements look. Color, size, and font are common properties. Each property has a value. Values change how properties work. Curly braces hold the properties and values together. The selector goes outside the braces.
Every element is a box. The box has four parts. The content is inside. Padding is around the content. It gives space. Border is around the padding. It adds lines. Margin is the outer space. It separates boxes. Adjusting these parts changes layout.
Web pages must fit all screens. Use media queries to change styles for different sizes. Media queries listen for screen width. They apply styles when the width matches. This makes pages easy to read. Users enjoy pages that fit their screens. Always test on phones and tablets.
Structuring Your Html
Using semantic elements helps in giving meaning to your HTML. These elements describe their purpose clearly. Examples include , , and . They make your code cleaner. Also, they help search engines understand your content better.
Organize your content for easy reading. Use headings to break up sections. This keeps everything neat. Short paragraphs work best. They help users find information quickly. Lists are also helpful. They make details easy to scan. Keep your text simple and clear.
Credit: www.wordstream.com
Styling With Css
Choose fonts that are easy to read. Sans-serif fonts are best for websites. Adjust font size for headers and paragraphs. Use consistent spacing for text. This helps make reading easy. Different font weights can show importance. Bold important words. Italics can show emphasis.
Select colors that match your brand. Use a color palette for harmony. Limit the number of colors. Too many colors are confusing. Backgrounds can be solid or have images. Make sure text is readable over backgrounds. Contrast helps with readability.
Layouts should be simple. Use grids for alignment. Grids help organize content. They make pages look neat. Responsive grids work on all devices. They adjust to screen sizes. Keep layout consistent across pages. This helps users navigate easily.
Enhancing User Experience
Adding interactive elements makes a landing page fun. Buttons that change color can be exciting. Pop-ups can share more information. These elements keep visitors engaged. They help in guiding users to important areas. A simple hover effect on images can be magical. Interactive forms also collect user data easily.
Animations bring life to a page. They make content more dynamic. Transitions help switch between sections smoothly. A slow fade-in effect is calming. Quick slide-ins grab attention. These elements create a flow in the design. Users feel more connected with the content. Animations should be smooth and not too fast.
Optimizing For Performance
Use only the CSS you need. This makes the page load faster. Remove any unused CSS from your files. Try to keep your CSS files small. Smaller files mean quicker loading.
Combine multiple CSS files into one. This reduces the number of requests. Fewer requests mean better loading speed. Think about using CSS minification tools. These tools make your CSS files even smaller.
Prioritize important CSS that loads first. This ensures the page looks good quickly. Consider using inline CSS for crucial styles. This reduces the wait time for users.
Use lazy loading for images and videos. This method delays loading until needed. It improves the overall speed. Try to keep your code neat and tidy. Clean code helps browsers understand it faster.
Testing And Debugging
Landing pages can have layout problems. Elements might not align properly. It’s important to check cross-browser compatibility. Different browsers show pages differently. Sometimes, fonts don’t load correctly. This makes the text look odd. Images might not appear. They can be too big or too small.
CSS validators help find errors. They show mistakes in your code. Browser developer tools are useful. These tools help inspect elements. Debugging tools can fix issues. They offer solutions for problems. Use them to see how your page looks. Check for any responsive design issues. Make sure it works on all devices.
Credit: www.freecodecamp.org
Best Practices
Keep your CSS code organized and consistent. Use the same naming style throughout. It helps others understand your code. Write code that is easy to read. Avoid long and messy lines. Use spaces and indentations. This makes your code clean.
Use comments to explain tricky parts. Comments help when you forget why you wrote something. They also help others who read your code. A neat code saves time later. It also prevents mistakes.
Make sure your page is accessible to everyone. Use colors that people can see clearly. Avoid using only colors to show important info. Some people can’t see colors well. Use text labels too.
Ensure your text is big enough. Small text is hard to read. Use headers to separate sections. Headers help people find info quickly. Accessibility is important for all users. It makes your page better for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Create A Landing Page?
To create a landing page, choose a clear goal and design a simple, responsive layout. Use engaging headlines, persuasive copy, and strong visuals. Incorporate a compelling call-to-action and ensure fast loading times. Test and optimize for better conversions. Utilize SEO techniques to improve search visibility.
How To Create A Home Page In Css?
To create a home page in CSS, start by setting up the HTML structure. Use CSS to style elements like headers, navigation, and sections. Choose colors, fonts, and layout styles. Ensure responsiveness with media queries. Test across different browsers for compatibility.
How To Make A Travel Website Using Html And Css?
Begin by creating an HTML file for structure. Use CSS for styling. Include travel-related images, text, and links. Ensure responsive design for mobile compatibility. Use semantic tags for accessibility. Test and optimize for performance and search engine visibility.
How Do I Create A Dynamic Landing Page?
To create a dynamic landing page, use a responsive design. Integrate interactive elements like videos and forms. Personalize content based on user data. Utilize A/B testing to optimize performance. Ensure fast loading speed for better user experience.
Conclusion
Creating a CSS-based landing page isn’t difficult. Start with clear goals. Use simple and clean design. Prioritize user experience. Incorporate responsive design for all devices. Keep testing and refining. Aim for fast loading times. Focus on engaging content. Ensure easy navigation for users.
Consistency in style builds trust. Remember, practice makes perfect. Each step helps improve skills. Soon, you’ll create effective landing pages. Your audience will appreciate the effort. Happy designing!






